For many years, the seek for extraterrestrial life has revolved round a easy rule: observe the water. If a distant planet has liquid water, and maybe oxygen, it’s flagged as probably liveable. However new analysis led by scientists at ETH Zurich means that this long-standing technique could also be incomplete. A planet can have oceans and continents, the researchers argue, and nonetheless be chemically incapable of supporting life. The actual constraint might lie a lot deeper, within the chemistry of a planet’s formation.
A Chemical Goldilocks Zone beneath the floor
The research, printed in Nature Astronomy beneath the title “The chemical habitability of Earth and rocky planets prescribed by core formation”, was led by Dr Craig R. Walton, a postdoctoral researcher on the Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life at ETH Zurich, alongside Professor Maria Schönbächler and colleagues. Their central declare is exact: life relies upon not simply on water and oxygen, however on whether or not two crucial parts, phosphorus and nitrogen, remained accessible in a planet’s mantle throughout its earliest formation. Phosphorus is required to construct DNA and RNA, the molecules that retailer and transmit genetic info. It additionally performs a key function in mobile power methods. Nitrogen, in the meantime, is an integral part of proteins, the structural and useful constructing blocks of cells. With out each, life “as we all know it merely can’t type”.
Phosphorus and nitrogen are crucial for all times: phosphorus kinds DNA, RNA, and ATP for power, whereas nitrogen builds proteins./ AI Illustration
“In the course of the formation of a planet’s core, there must be precisely the correct amount of oxygen current in order that phosphorus and nitrogen can stay on the floor of the planet,” Walton defined. Younger rocky planets start as molten our bodies. As they cool, heavy parts reminiscent of iron sink to type the core, whereas lighter materials kinds the mantle and crust. On the identical time, oxygen ranges decide how parts chemically partition between metallic and rock. If oxygen is scarce, phosphorus bonds with iron and sinks into the core, successfully eradicating it from the floor surroundings. If oxygen is just too ample, phosphorus stays within the mantle, however nitrogen is extra more likely to escape into the ambiance and ultimately be misplaced to house. “Having an excessive amount of or too little oxygen within the planet as an entire – not within the ambiance per se – makes the planet unsuitable for all times as a result of it traps key vitamins for all times within the core,” Walton informed the Every day Mail. “A unique oxygen stability means you don’t have anything to work with left on the floor when the planet cools and also you type rocks.” Utilizing numerical modelling, the crew recognized what they describe as a really slender “chemical Goldilocks zone,” an intermediate oxygen vary through which each phosphorus and nitrogen stay within the mantle in portions adequate for all times.

A planet’s ‘Goldilocks zone’ for all times requires simply the correct amount of oxygen to maintain phosphorus and nitrogen out there/ Picture: X
“Our fashions clearly present that the Earth is exactly inside this vary,” Walton stated. “If we had had just a bit extra or rather less oxygen throughout core formation, there wouldn’t have been sufficient phosphorus or nitrogen for the event of life.” Earth seems to have struck that stability round 4.6 billion years in the past.
Rethinking what makes a planet liveable
The findings counsel that many planets beforehand thought of promising could also be chemically unsuitable for all times from the outset, even when they comprise water. Whereas no recognized life can survive with out liquid water, the researchers argue that utilizing oxygen or water alone as markers of habitability could also be deceptive. A planet’s complete oxygen stability throughout its formation, not merely atmospheric oxygen, determines whether or not life-critical parts stay out there. Walton warned that this may occasionally considerably slender the variety of liveable worlds within the universe. He steered there could also be only one to 10 per cent as many liveable planets as beforehand estimated. “It might be very disappointing to journey all the way in which to such a planet to colonise it and discover there isn’t any phosphorus for rising meals,” he stated. “We’d higher attempt to verify the formation situations of the planet first, very similar to guaranteeing your dinner was cooked correctly earlier than you go forward and eat it.” Nearer to residence, the analysis means that Mars lies simply outdoors this chemical zone. Mars seems to comprise comparatively ample phosphorus, however considerably decrease nitrogen ranges close to the floor. As well as, harsh salts and different floor chemistry make the soil inhospitable.
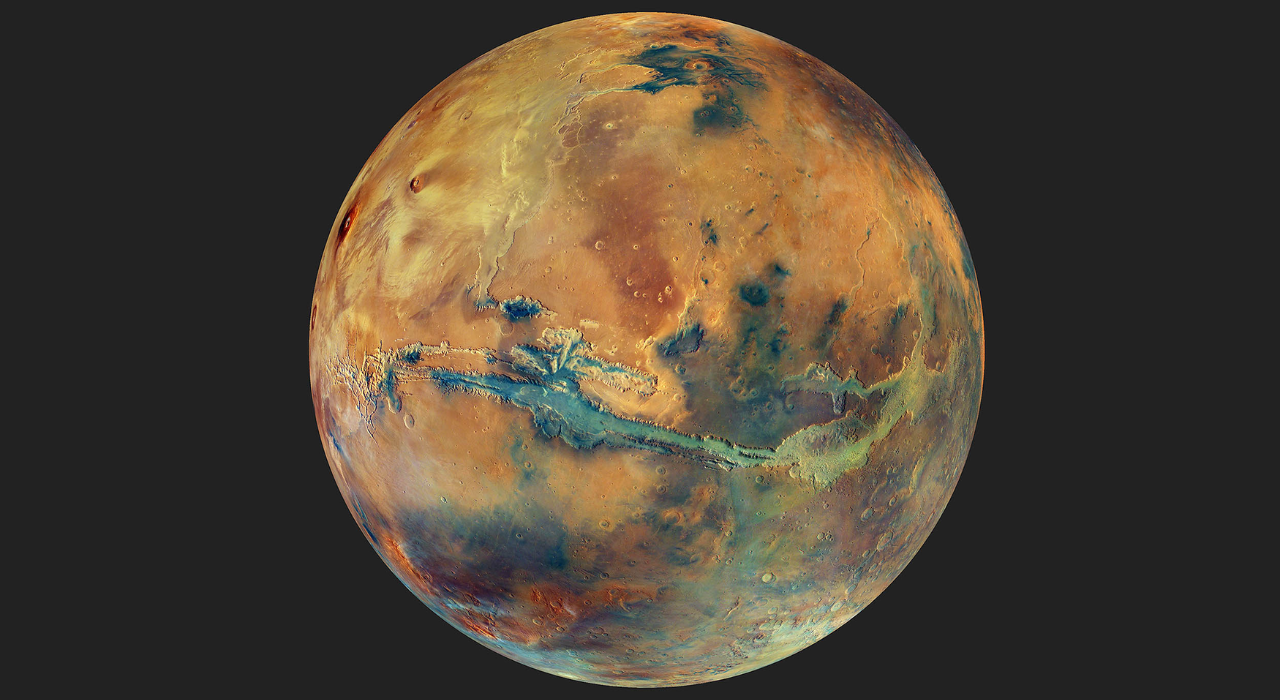

Mars has sufficient phosphorus however lacks adequate nitrogen, making its floor chemically unsuitable for supporting life as on Earth/ Mars in its true coloration/ Picture: Earth.com
“Mars is pretty just like Earth, and its formation situations imply there’s extra phosphorus, not much less. This implies rising meals there is likely to be comparatively simple,” Walton stated. However he added that the nitrogen deficit and floor chemistry pose main challenges: “It isn’t that totally different, however it isn’t at the moment liveable, Elon Musk should give you a intelligent technique to change the composition to develop meals there.”
Looking out the proper stars
Immediately measuring the inner chemistry of distant rocky planets stays extraordinarily tough. Nonetheless, astronomers can infer doubtless planetary compositions by learning host stars. Planets type from the identical materials as their dad or mum stars. The oxygen abundance and total chemical construction of a star subsequently form the composition of its planetary system. Photo voltaic methods whose stars intently resemble our Solar might supply higher odds. “This makes trying to find life on different planets much more particular,” Walton stated. “We should always search for photo voltaic methods with stars that resemble our personal Solar.” The work reframes the long-running seek for life past Earth. Water stays obligatory. Nevertheless it might not be sufficient. A planet’s destiny, whether or not sterile or dwelling, may hinge on a fragile chemical stability struck in its first molten moments, lengthy earlier than oceans, atmospheres or continents ever fashioned.




















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-MoldyBread-d706dcc1276643f1a60522e1cd83cdb4.jpg?w=120&resize=120,86&ssl=1)